Software reuse commonly occurs informally in many projects, where existing designs or code are adapted to meet project requirements. Reuse-oriented approaches rely on a repository of reusable components and an integrating framework for their composition.
This reuse-oriented model has two main subtypes of use. These reuses are-
Informal Reuse: Occurs spontaneously within a project. Developers identify and modify existing designs or code to fit project needs.
Formal Reuse: Involves a structured process and a repository of reusable components. Emphasizes the use of existing components and frameworks.
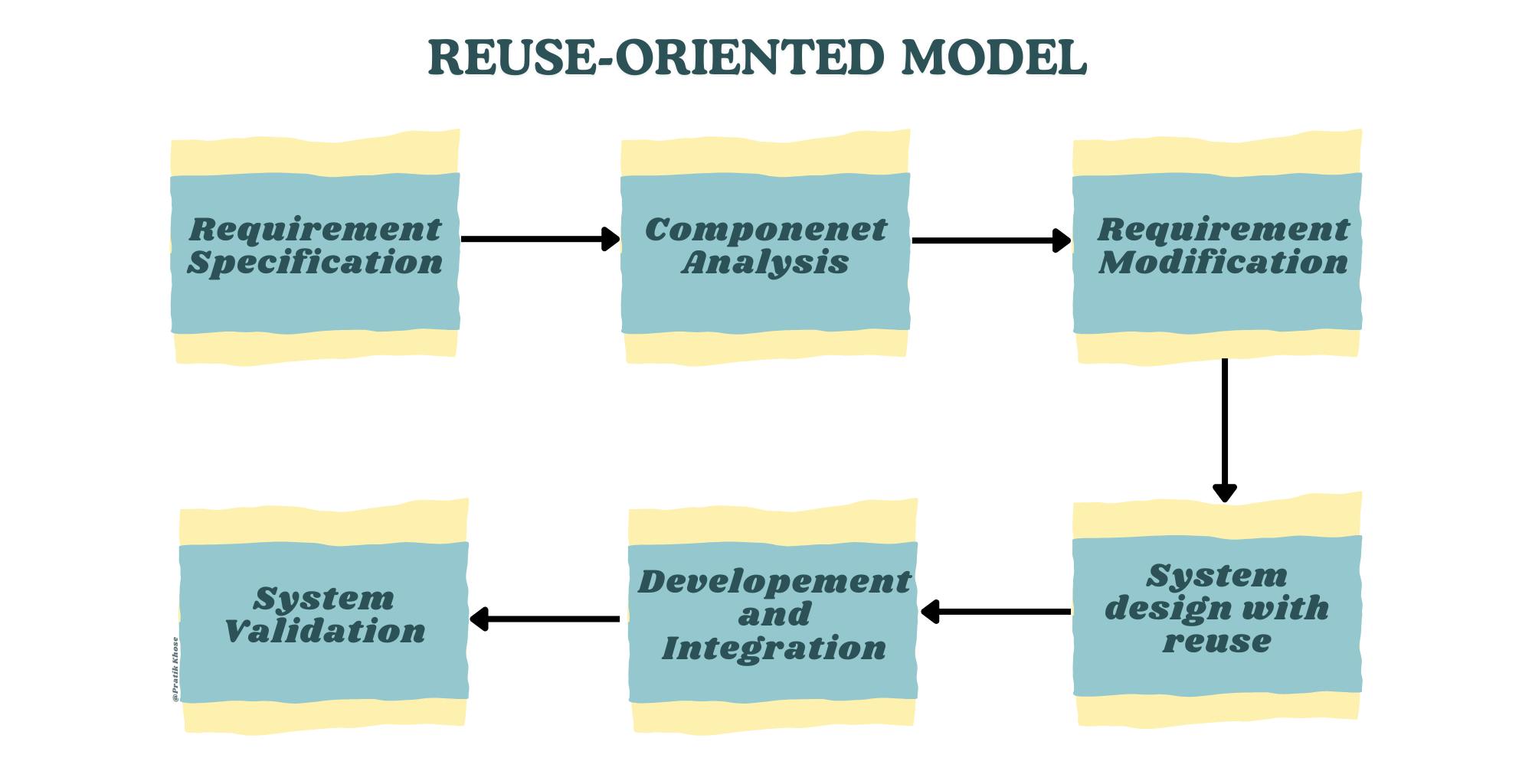
Reuse-Oriented Process Model has mainly four stages. Now let us understand about these stages in detail-
Software specification:
Defining what services are required from the system and identifying the constraints on the operation and development of the system.
This involves gathering and finalizing the requirements and all the statistical data required for the development of the software.
Component Analysis:
Search for components that can implement specified requirements.
Components may not provide exact matches, requiring modifications or alternative solutions.
Requirements Modification:
Analyze requirements based on discovered components.
Modify requirements to align with available components.
Re-enter component analysis if modifications are impossible.
System Design with Reuse:
Design or reuse a framework, considering the components to be reused.
New software design may be necessary if reusable components are unavailable.
Development and Integration:
Develop software that cannot be externally procured.
Integrate components and Commercial Off-The-Shelf (COTS) systems to create the new system.
System integration may be integrated into the development process.
Requirement validation:
The developed software is thoroughly checked to ensure that it aligns with the specified requirements and meets customer expectations.
Here the software is checked to ensure that it is what the customer requires.
Types of Reusable Components:
Web Services: Developed according to service standards and available for remote invocation.
Collections of Objects: Developed as a package for integration with component frameworks like .NET or J2EE.
Stand-Alone Software Systems: Configured for use in a specific environment.
Now let us understand the Advantages and Disadvantages ReuseOriented model:
Advantages:
Reduces development effort and costs.
Accelerates software delivery.
Disadvantages:
Inevitable requirements compromises may lead to a system not fully meeting user needs.
Some control over system evolution is lost as updates to reusable components are not under the user organization's control.
Reuse-oriented software engineering offers efficiency gains through the use of existing components but poses challenges in managing compromises and maintaining control over system evolution.